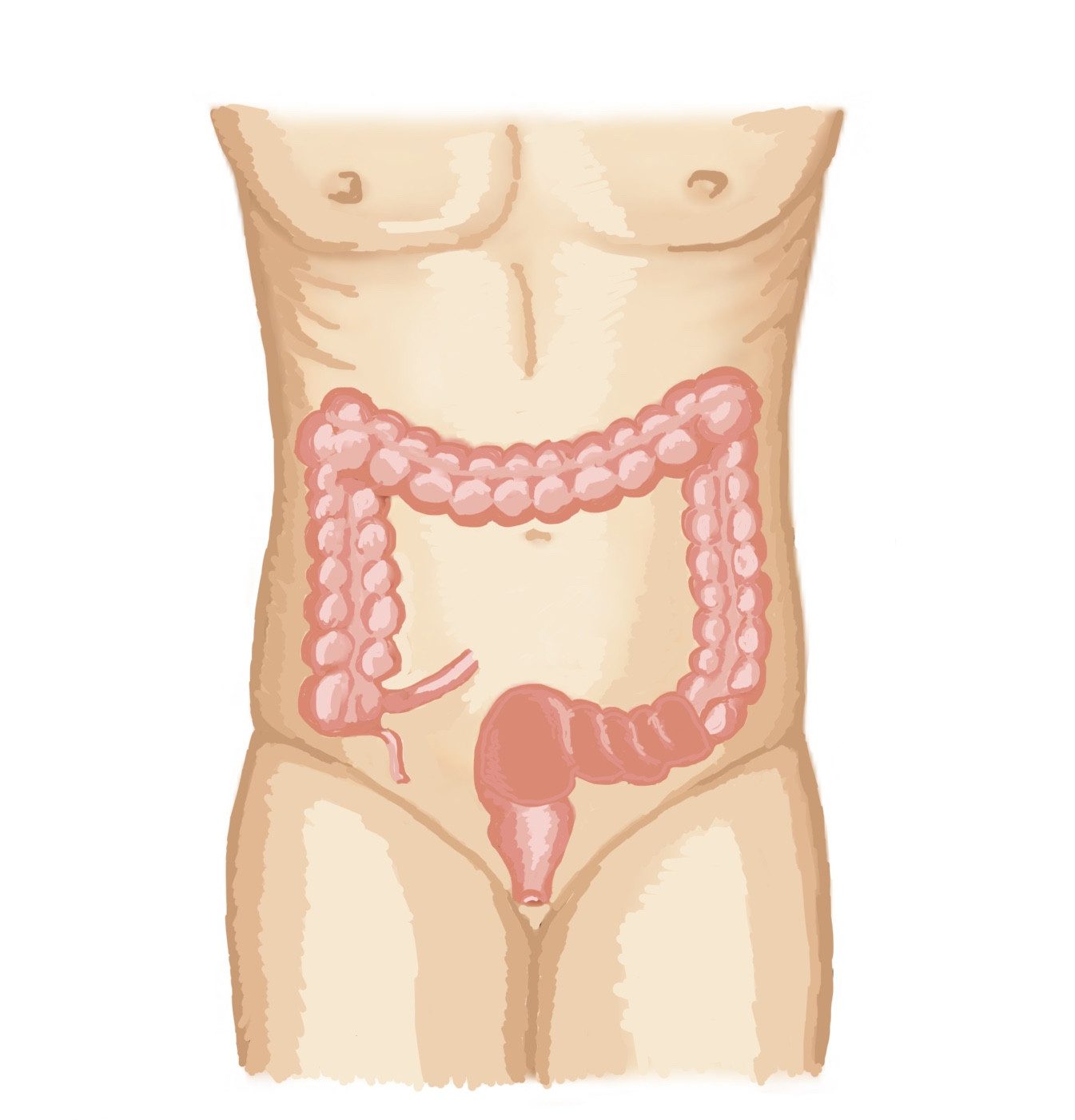
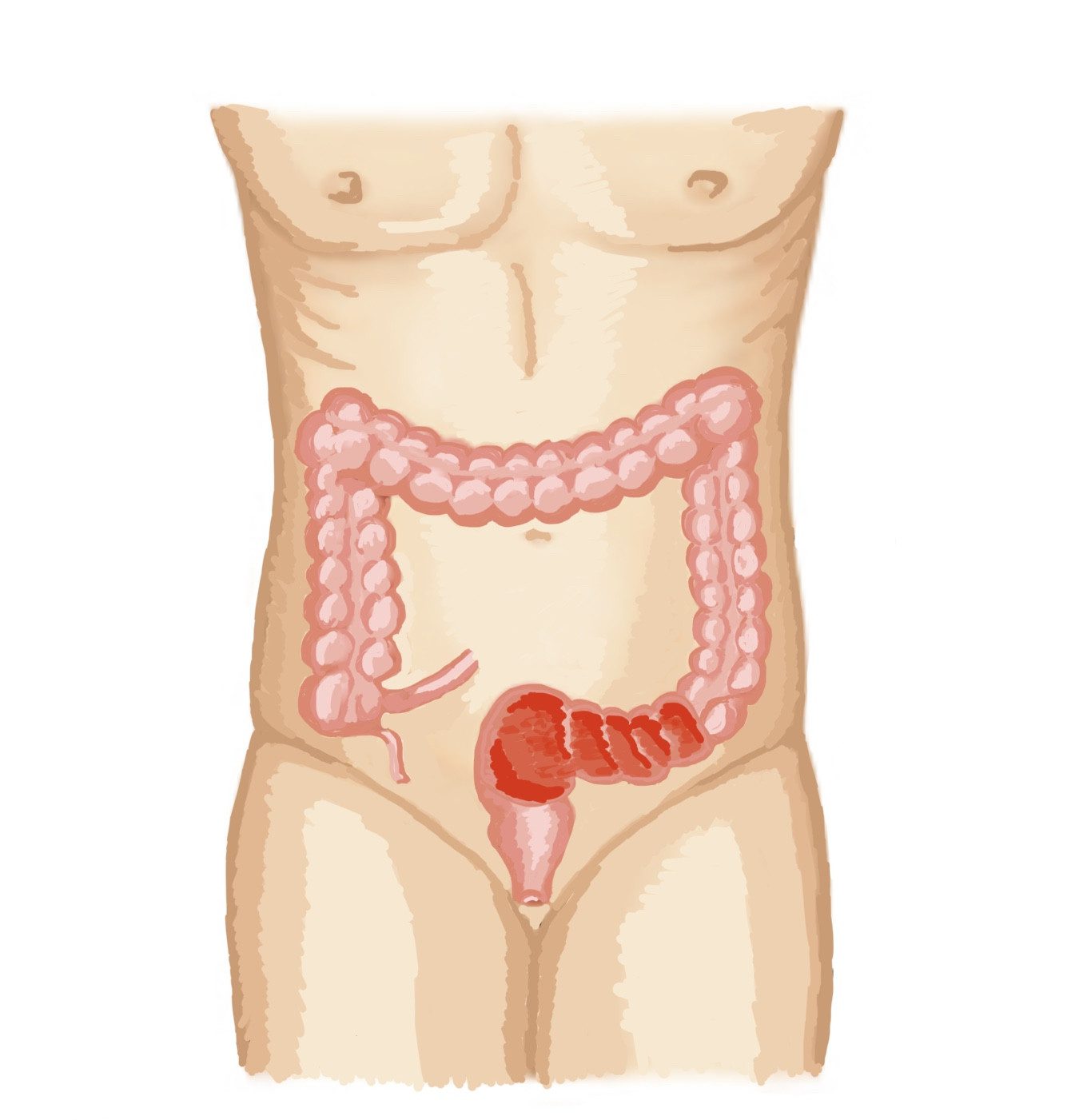
Colitis is the inflammation of the large bowel. Mostly comes with looser stools and urgent defecation. Several types are caused by several different agents.
Most important is to differentiate the infectious colitis from the so called IBD, inflammatory bowel disease. The former is caused by microorganisms, mostly as part of gastroenteritis (infection and inflammation of the whole gastrointestinal tract) and often settles by itself or on antibiotics. The latter is an exaggerated immune response, affected by hereditary factors and diet.
When colitis is suspected, and the stool test shows no infectious pathogens, colonoscopy is a must. During colonoscopy biopsy samples of the lining are taken to identify the type of inflammation. This then guides the treatment.
What signs and symptoms one has with this problem?
Colitis comes with looser stools (diarrhoea), often excess mucus (jelly like stuff) and maybe blood is seen in the stool. When the rectum is involved, its storing function is affected, it wants to get rid of the stools received from above causing a sense of urgency at defecation, sometimes to the level of difficulties with controlling the stool.