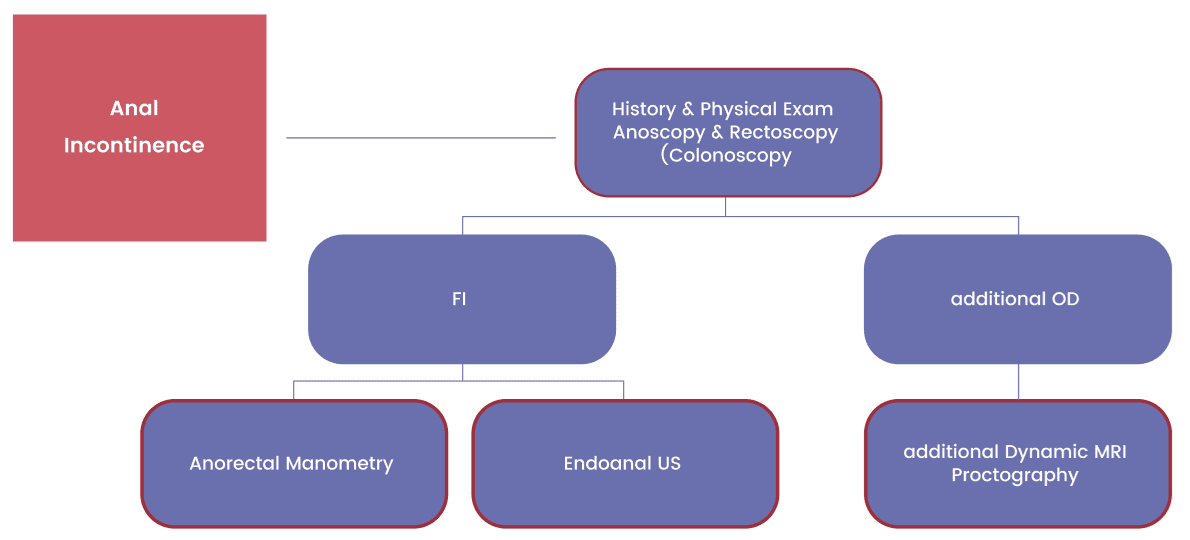
- 99 patients with FI (Fecal Incontinence) with or without OD (Obstructed Defecation)
- Gender: 68 females, 21 males
- Age: 36 – 64; mean 47.2
- Home
- /
- For colleagues




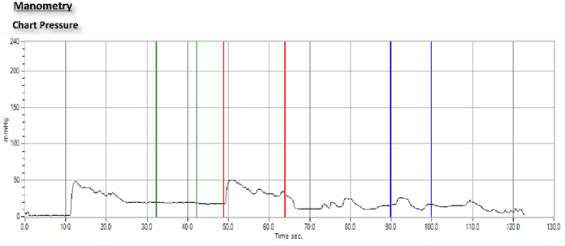
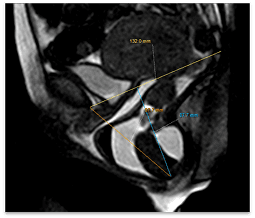
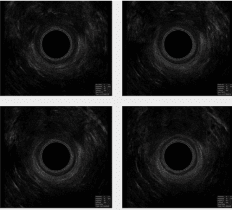
Conservative
Operative
FI
FI & OD
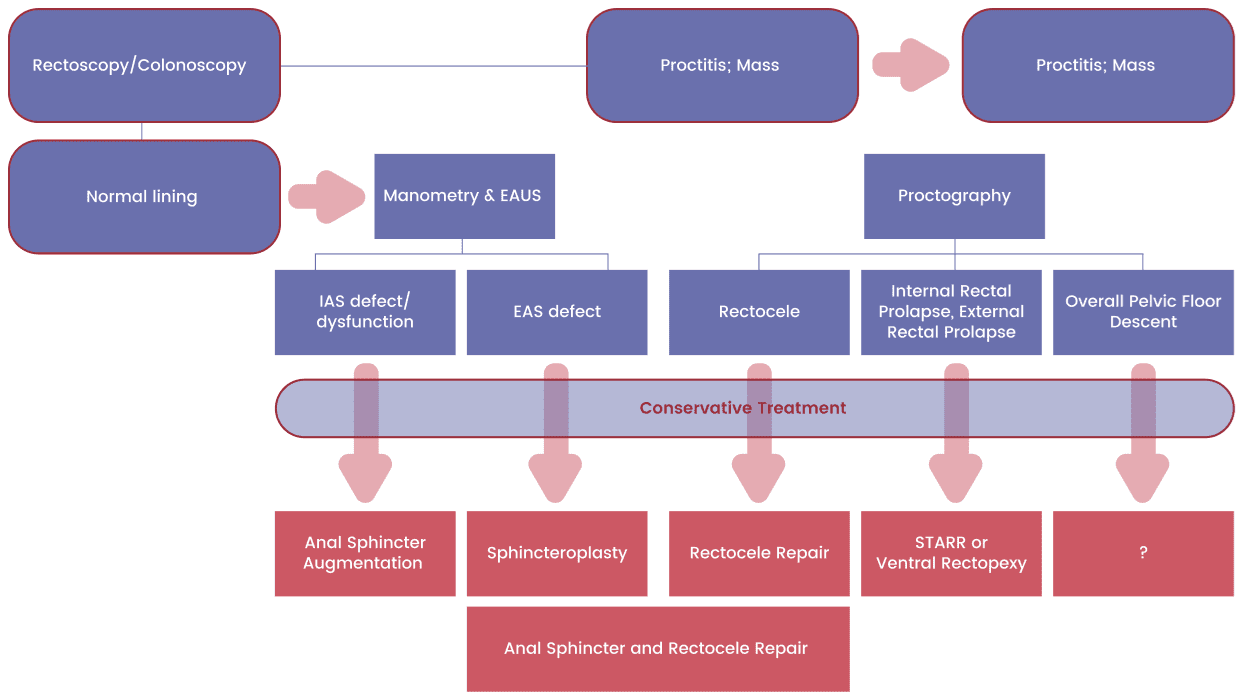
Of these 99 patient 19 had surgeries – 6 for both OD and FI; 5 for only FI and 3 for only OD
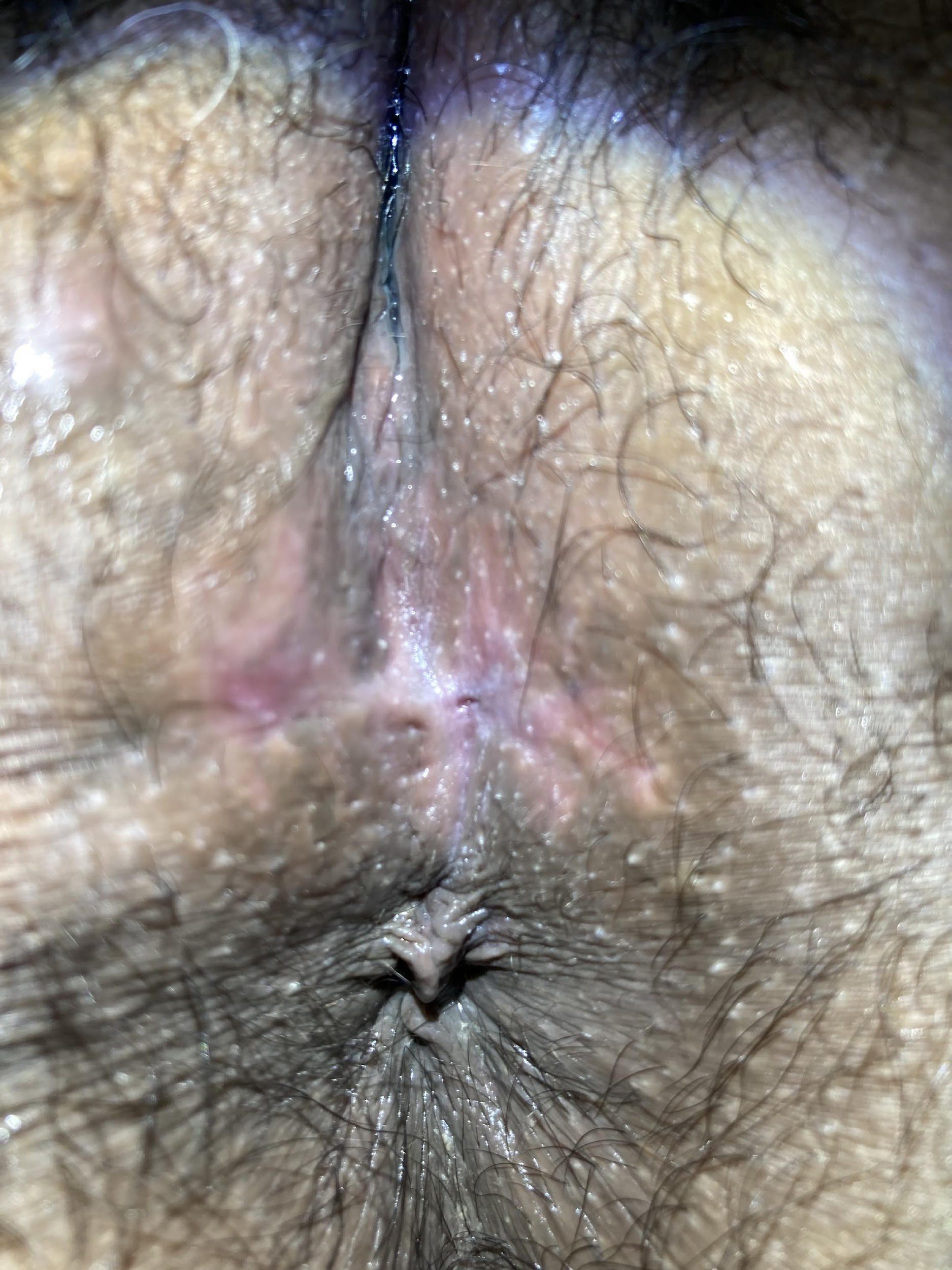
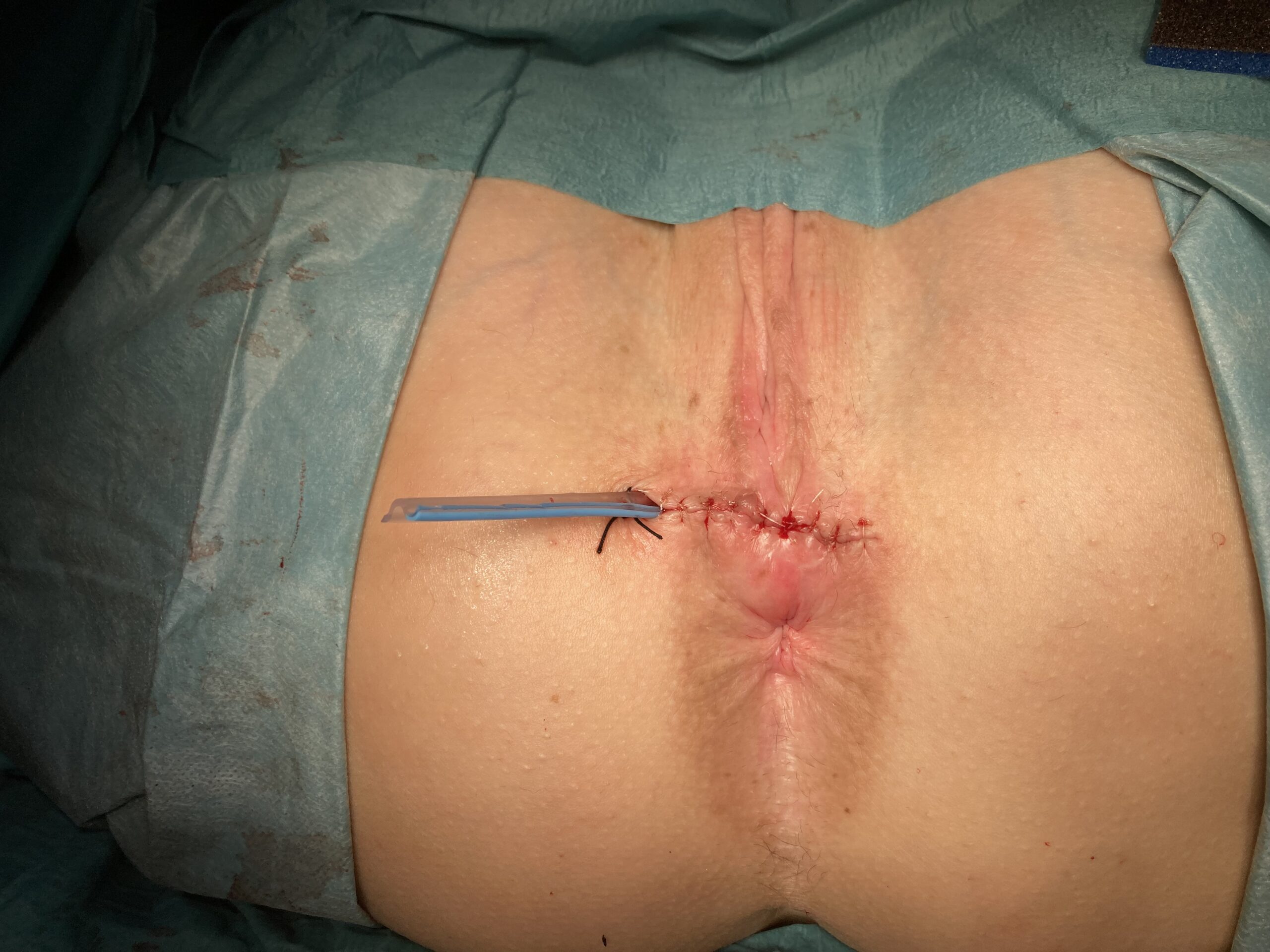
Sphinctero-plasty
these photos contain sensitive content which some people may find offensive and disturbing
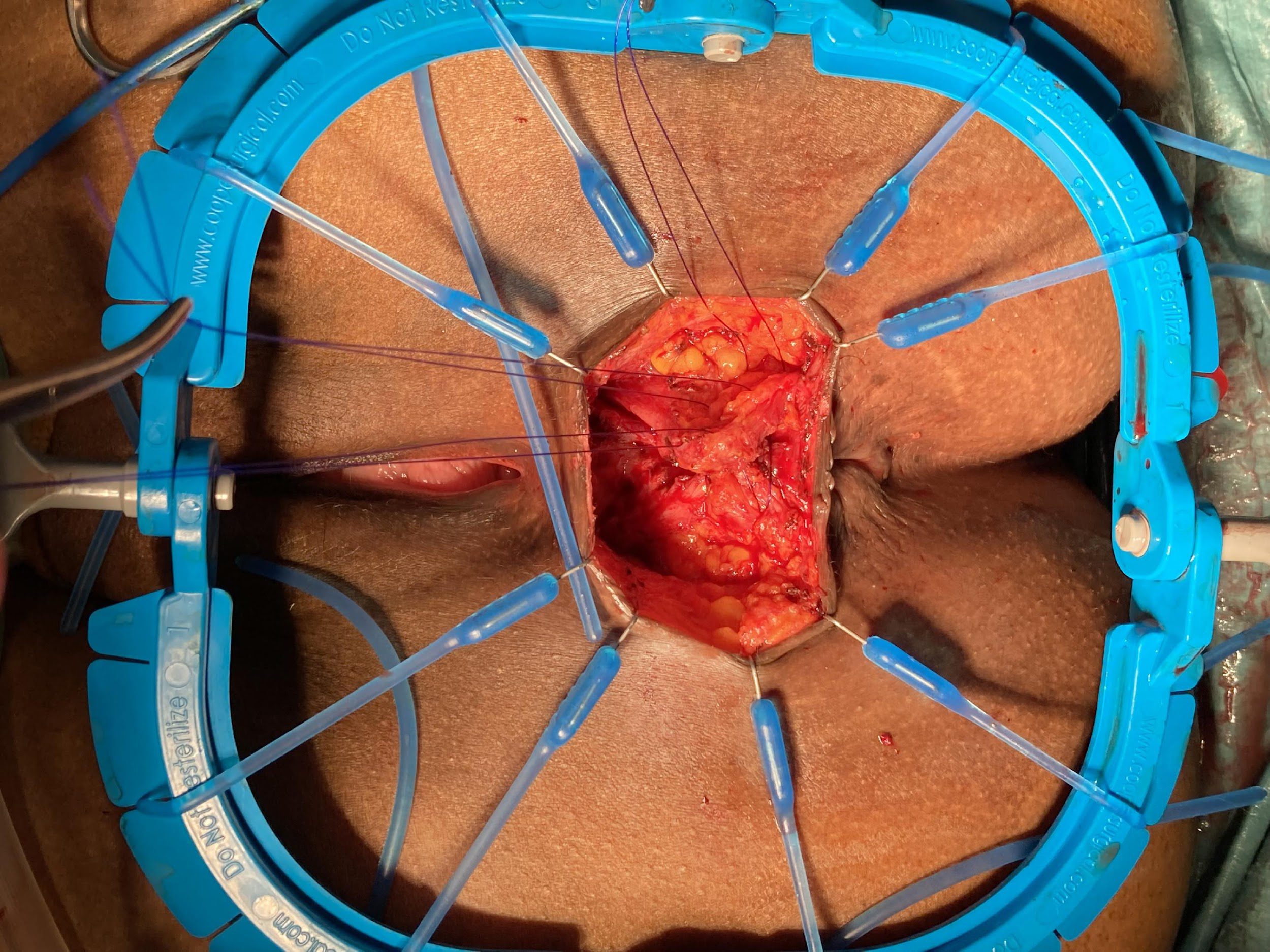
these photos contain sensitive content which some people may find offensive and disturbing
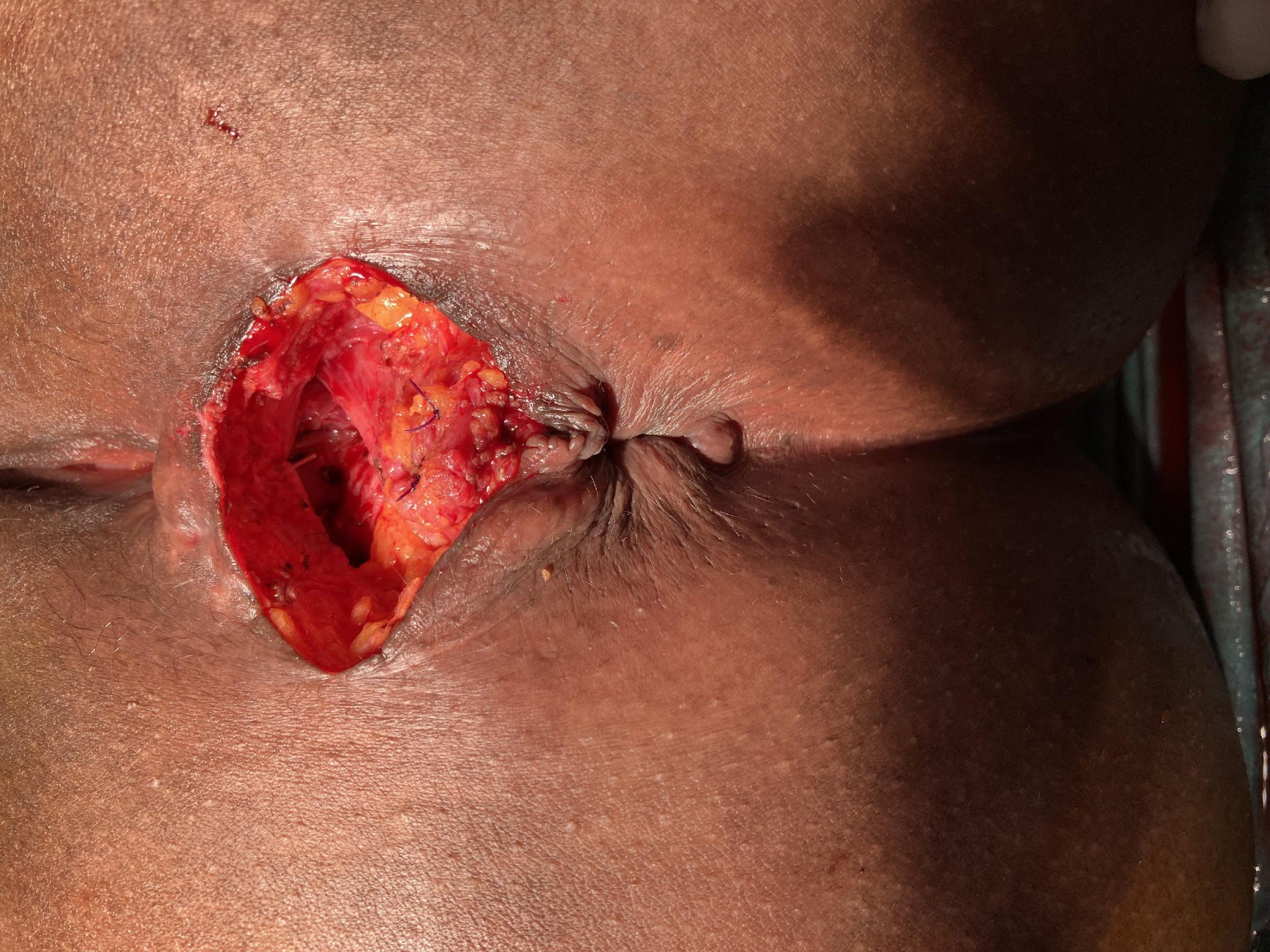
these photos contain sensitive content which some people may find offensive and disturbing
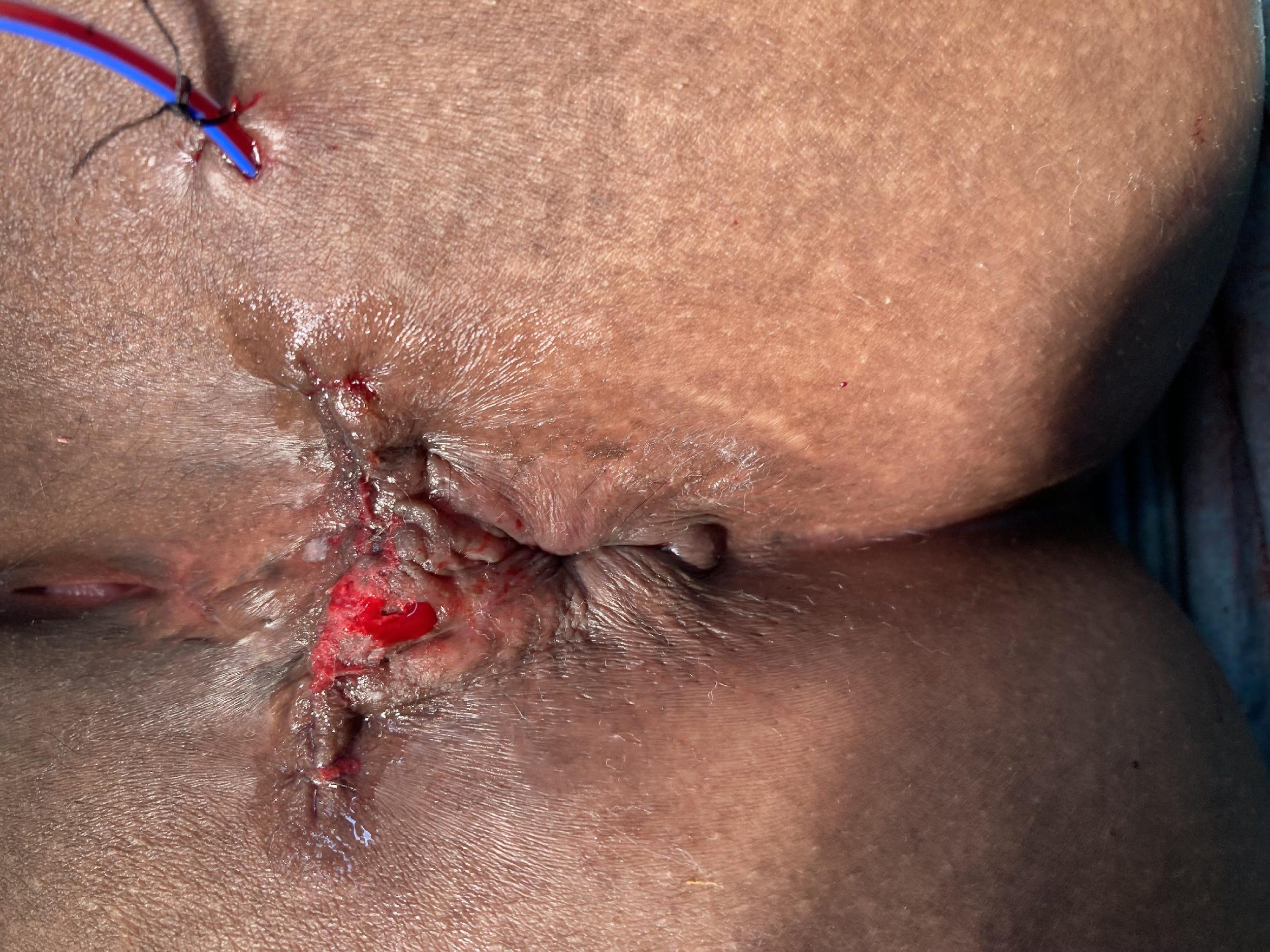
these photos contain sensitive content which some people may find offensive and disturbing
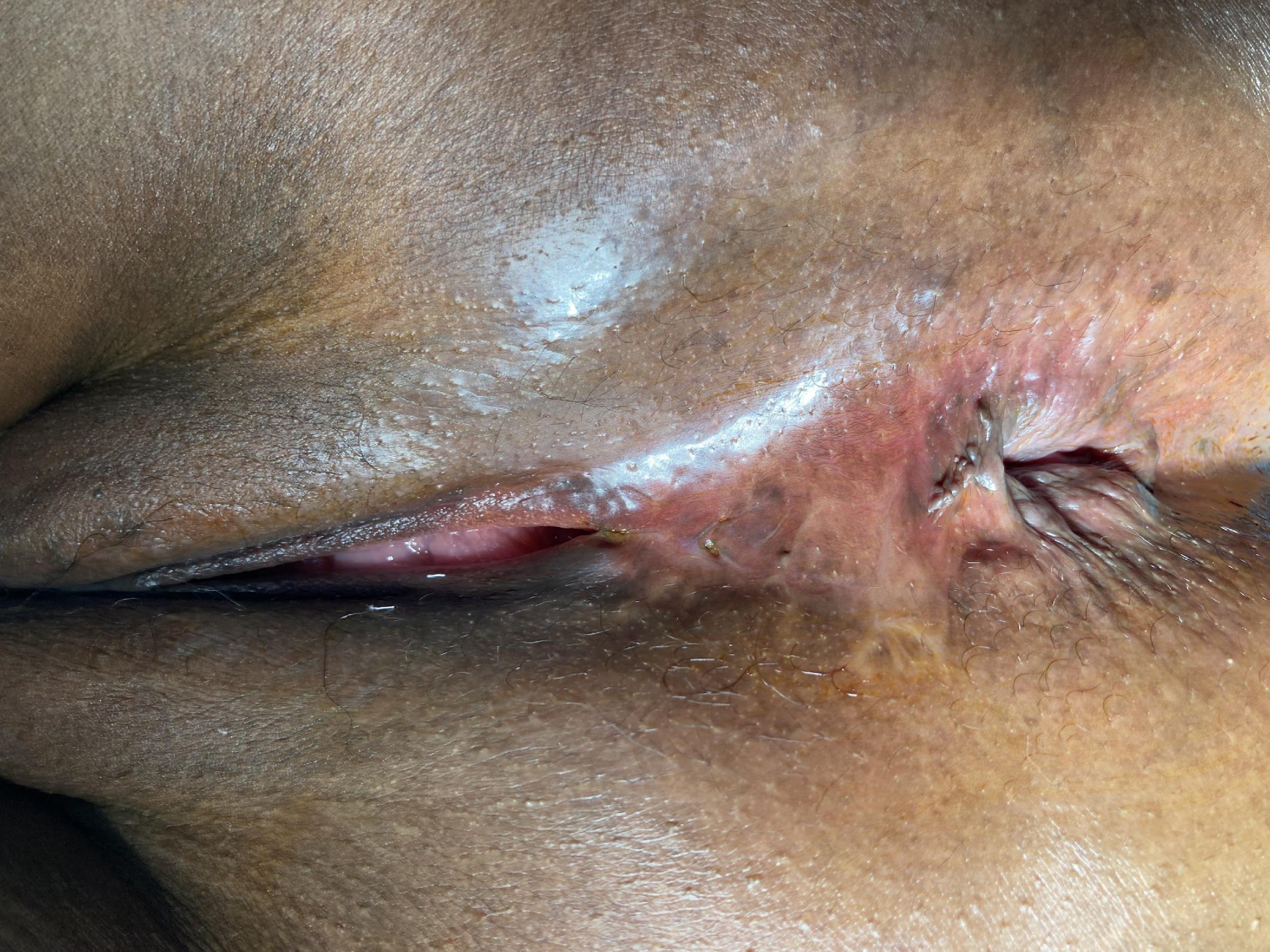
these photos contain sensitive content which some people may find offensive and disturbing
these photos contain sensitive content which some people may find offensive and disturbing
these photos contain sensitive content which some people may find offensive and disturbing
these photos contain sensitive content which some people may find offensive and disturbing
these photos contain sensitive content which some people may find offensive and disturbing
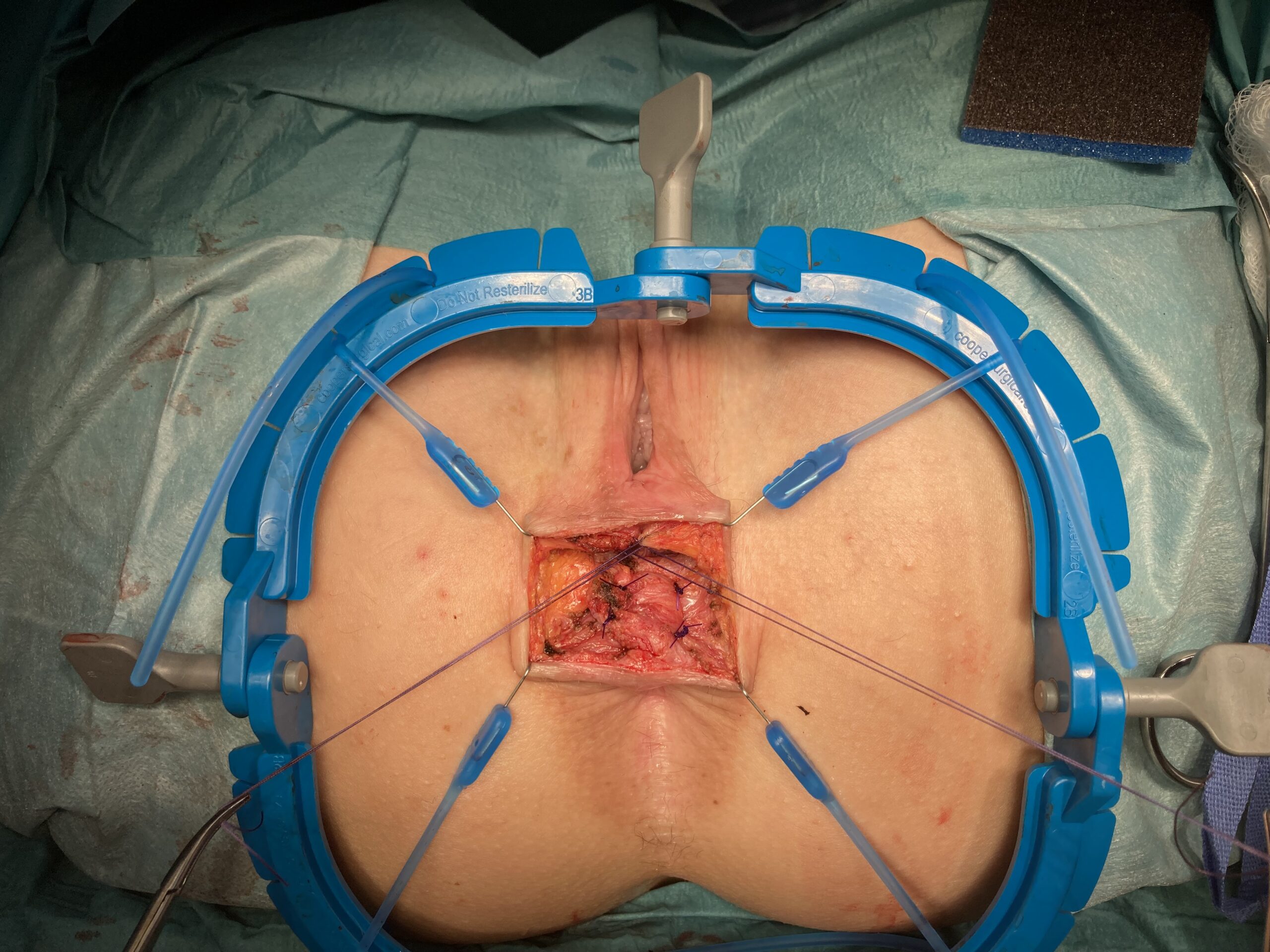
these photos contain sensitive content which some people may find offensive and disturbing
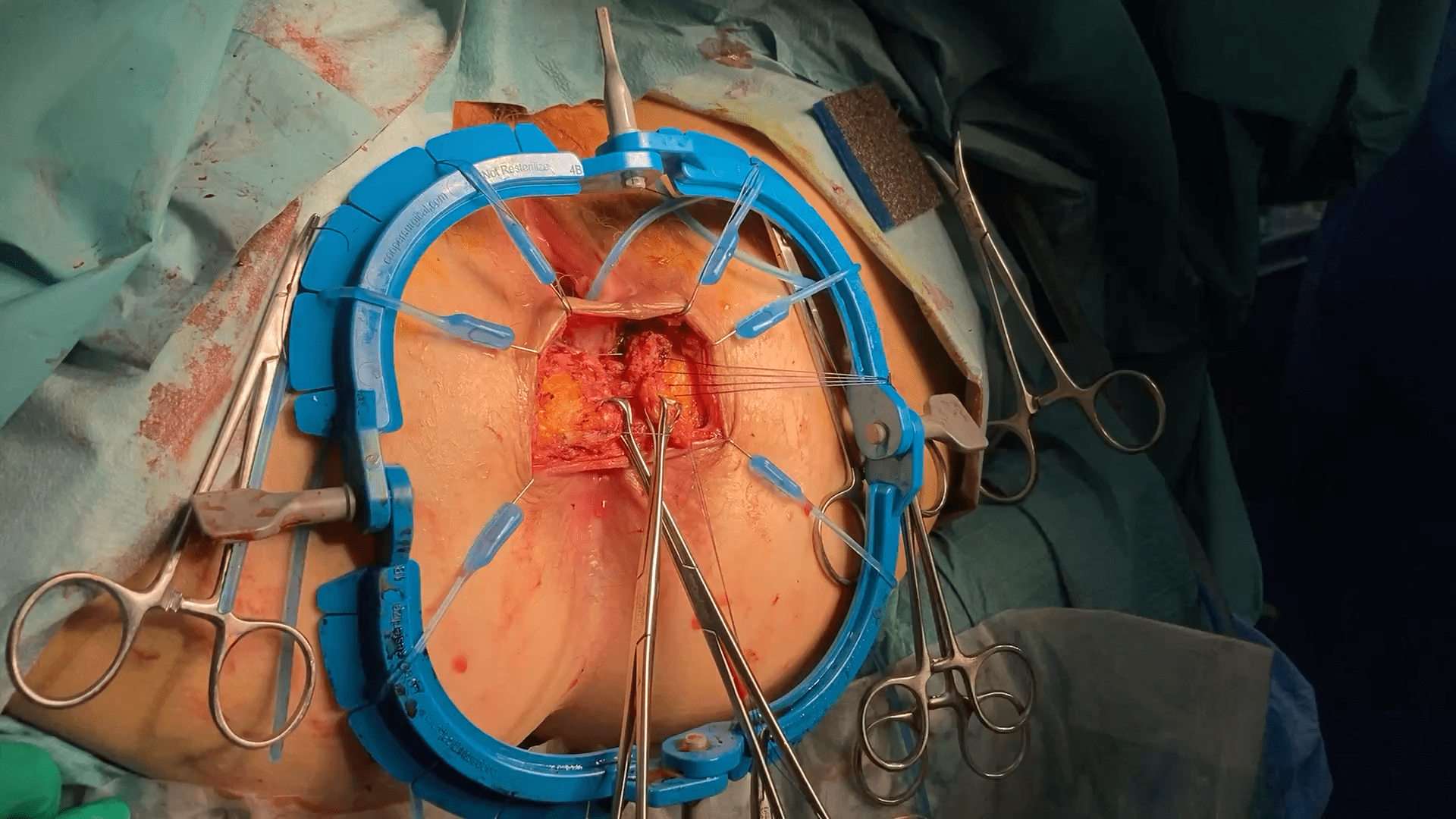
these photos contain sensitive content which some people may find offensive and disturbing
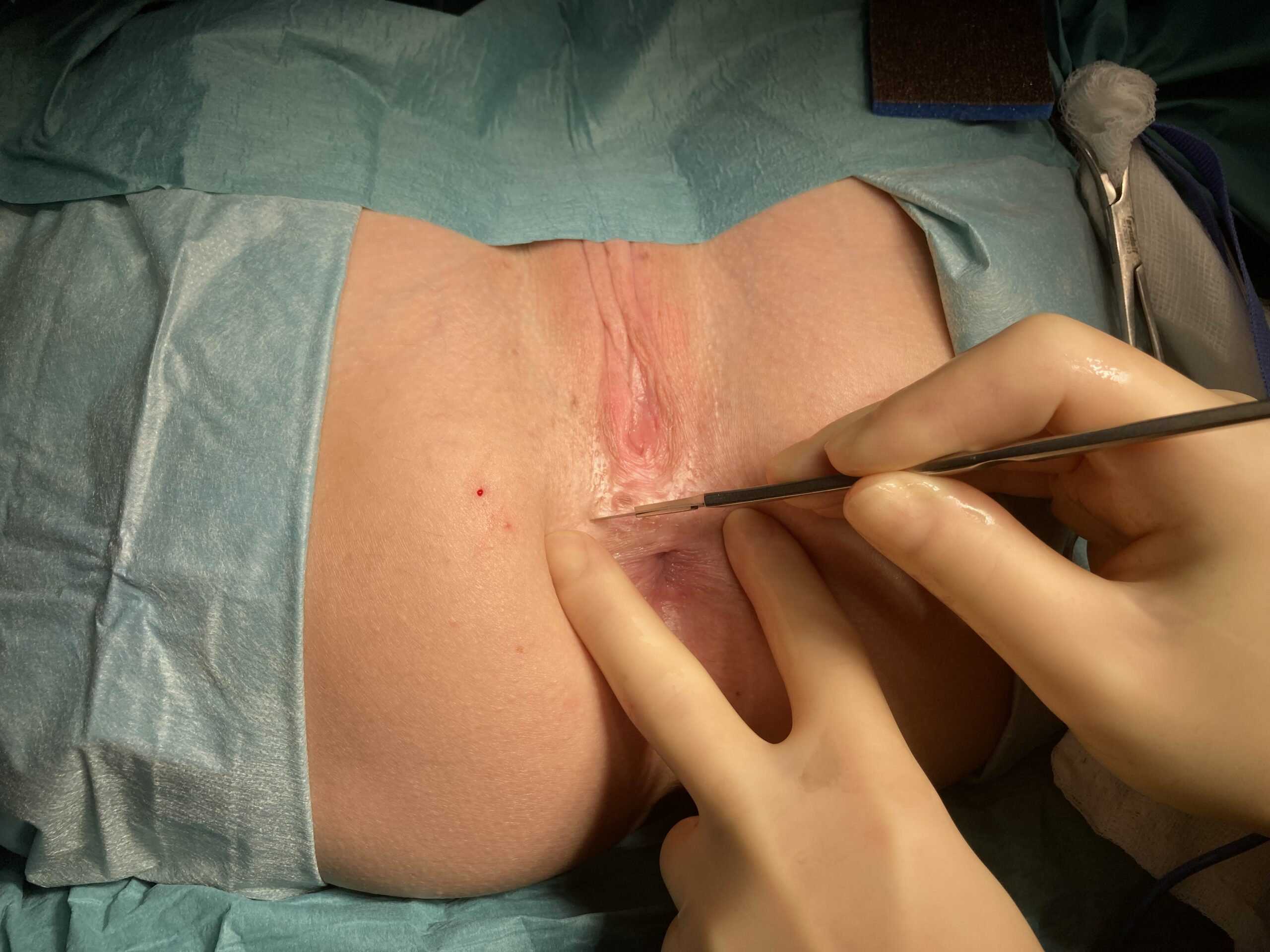
Sphinctero-plasty and Sphin-keeper together
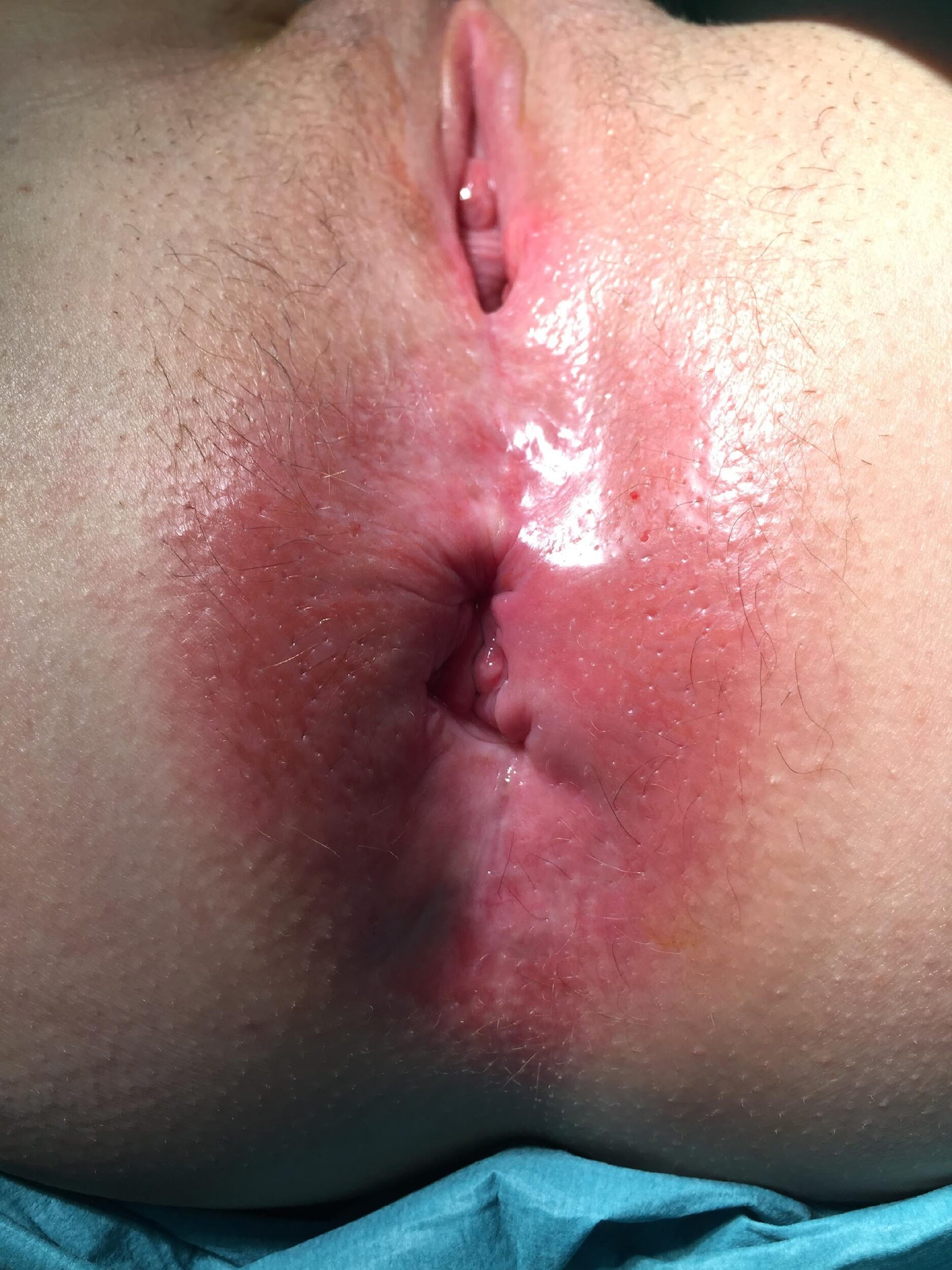
these photos contain sensitive content which some people may find offensive and disturbing
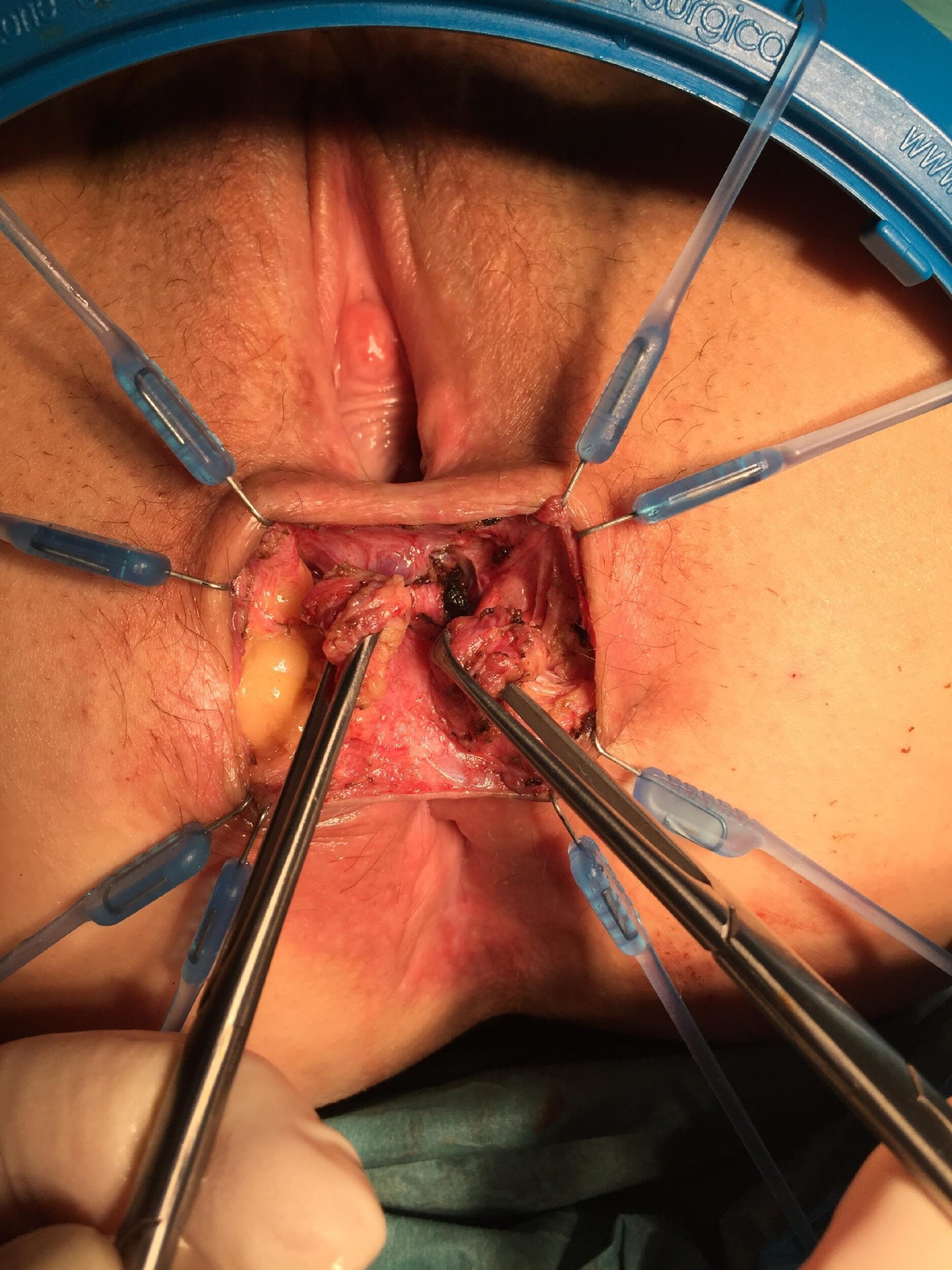
these photos contain sensitive content which some people may find offensive and disturbing
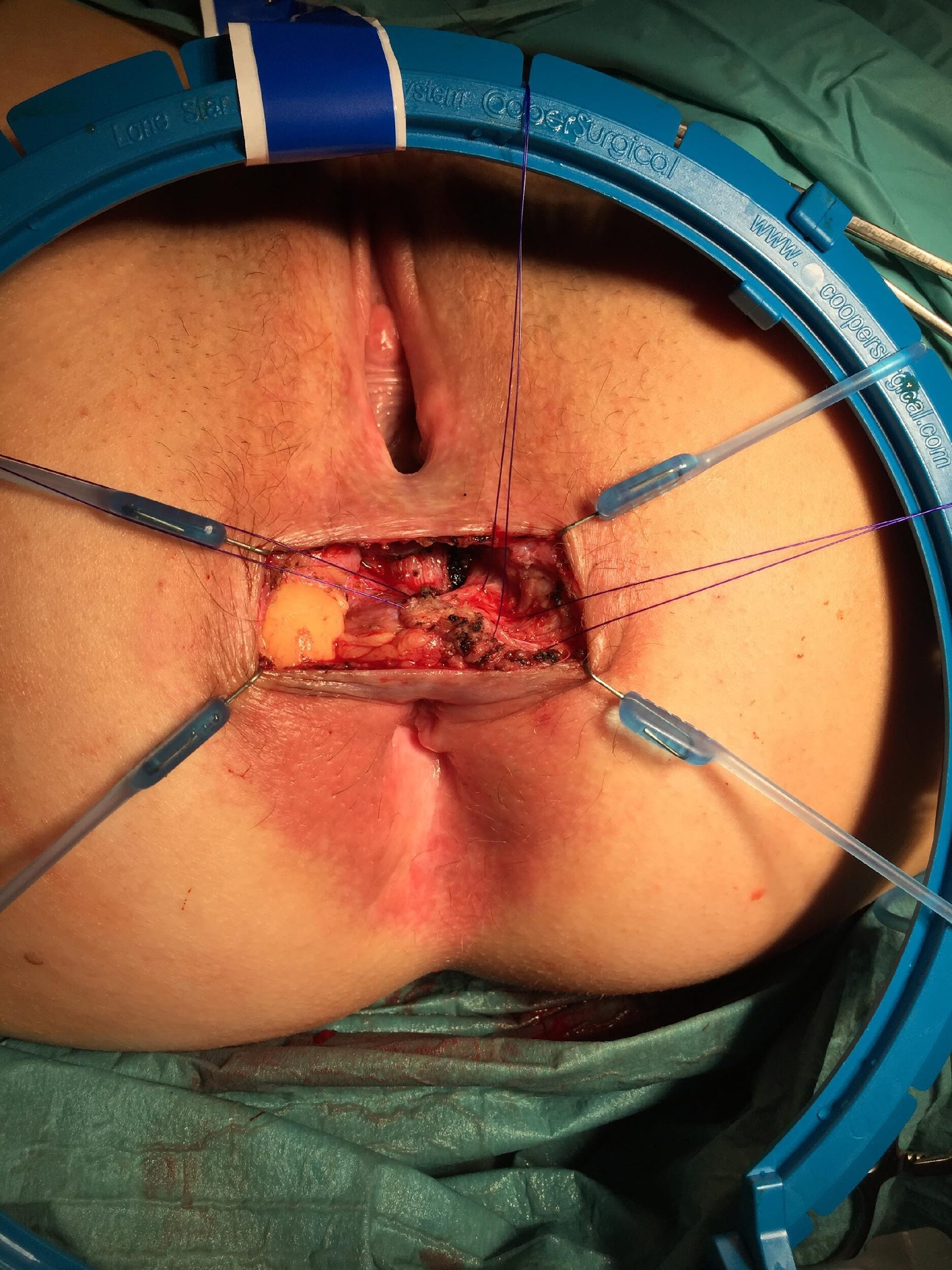
these photos contain sensitive content which some people may find offensive and disturbing
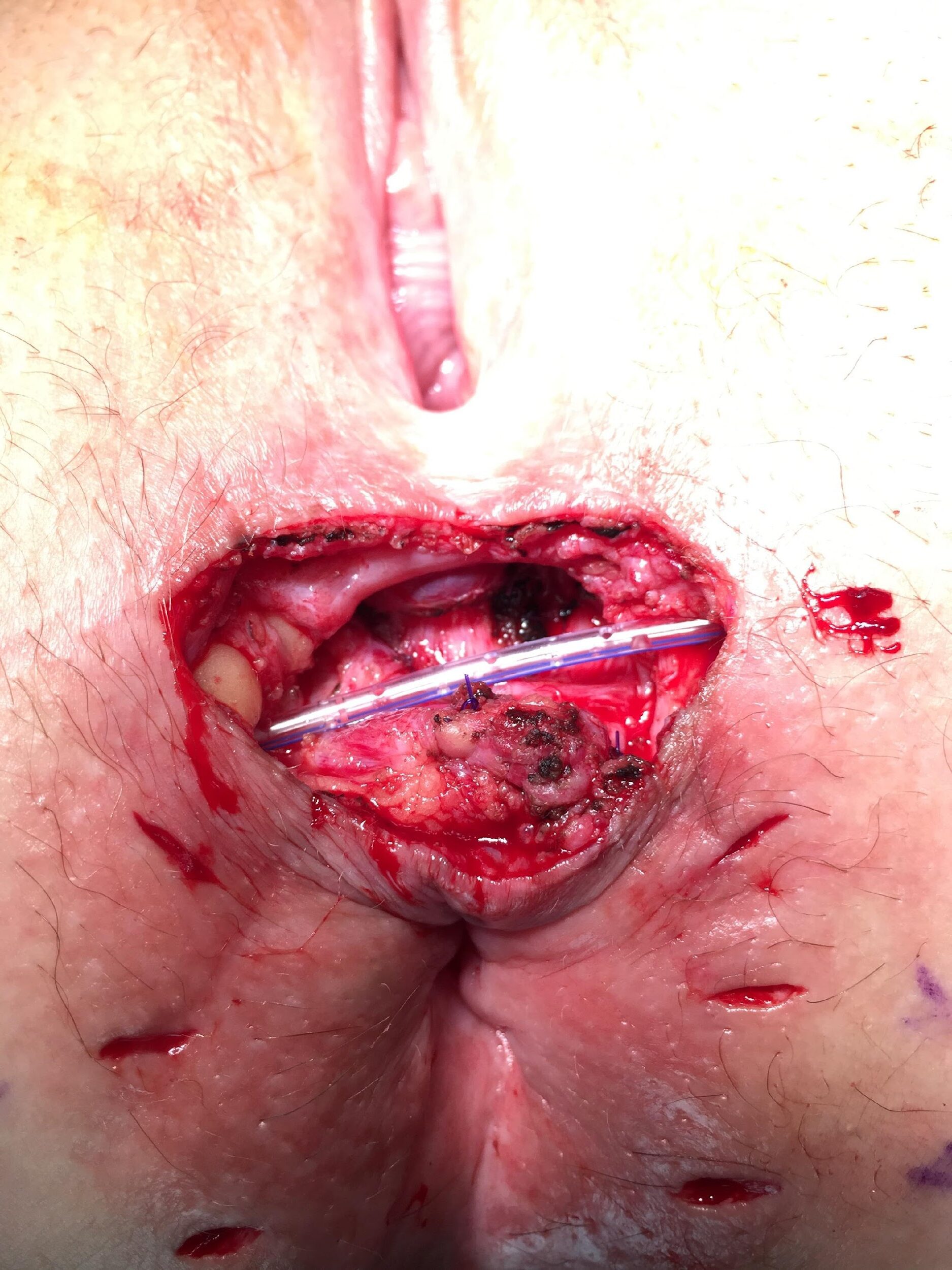
these photos contain sensitive content which some people may find offensive and disturbing
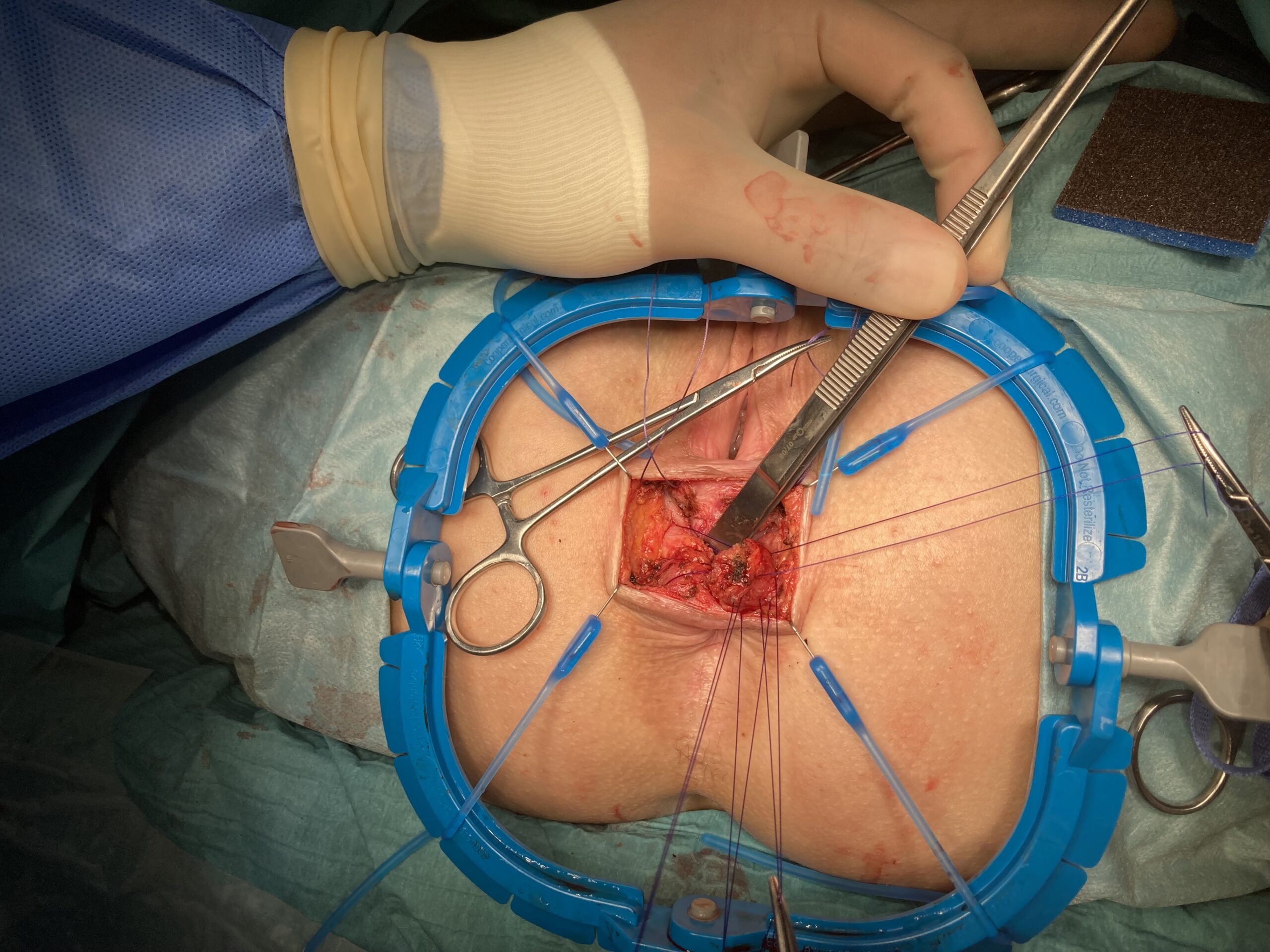
Repair of “Cloaca”
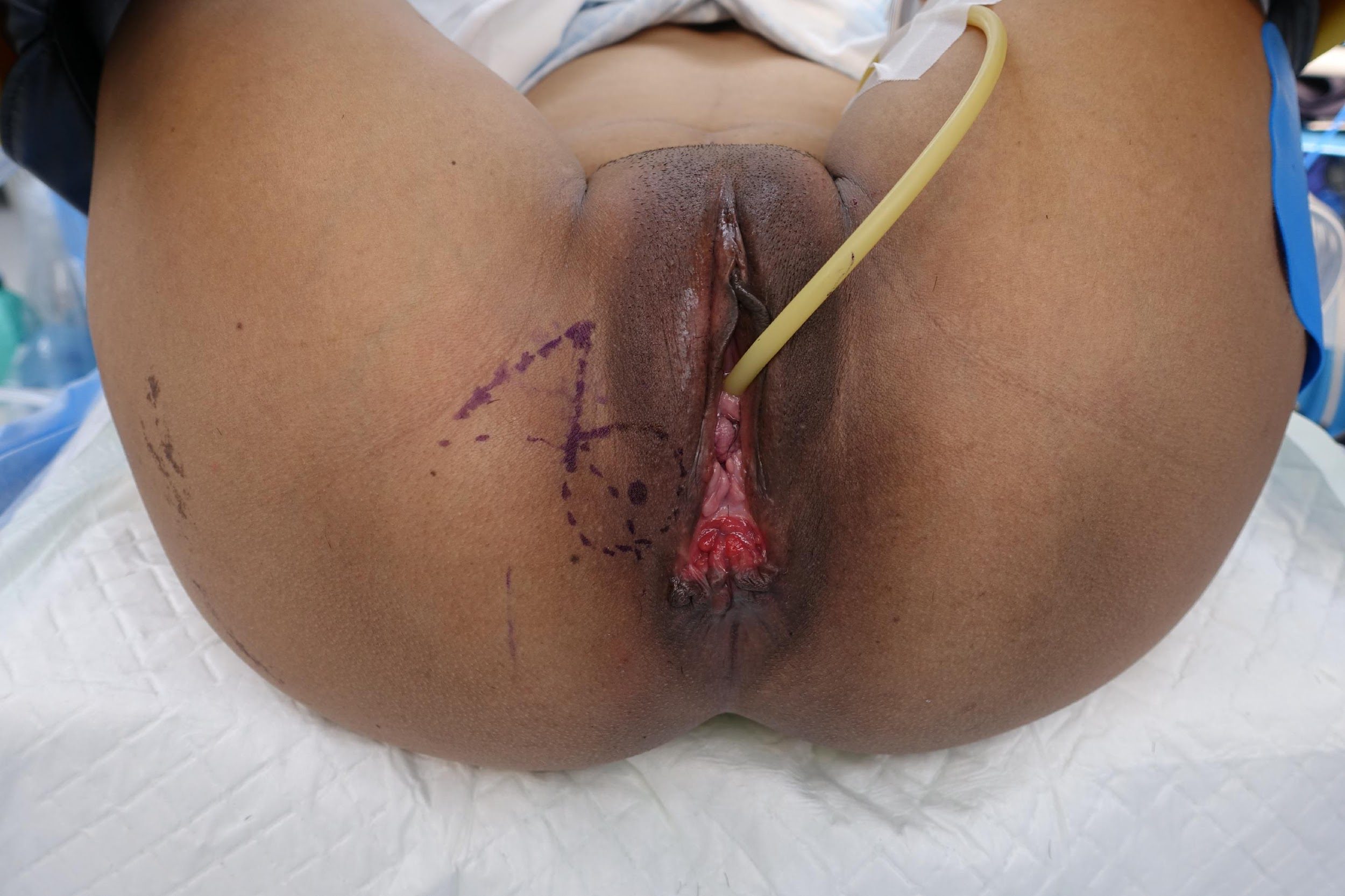
these photos contain sensitive content which some people may find offensive and disturbing
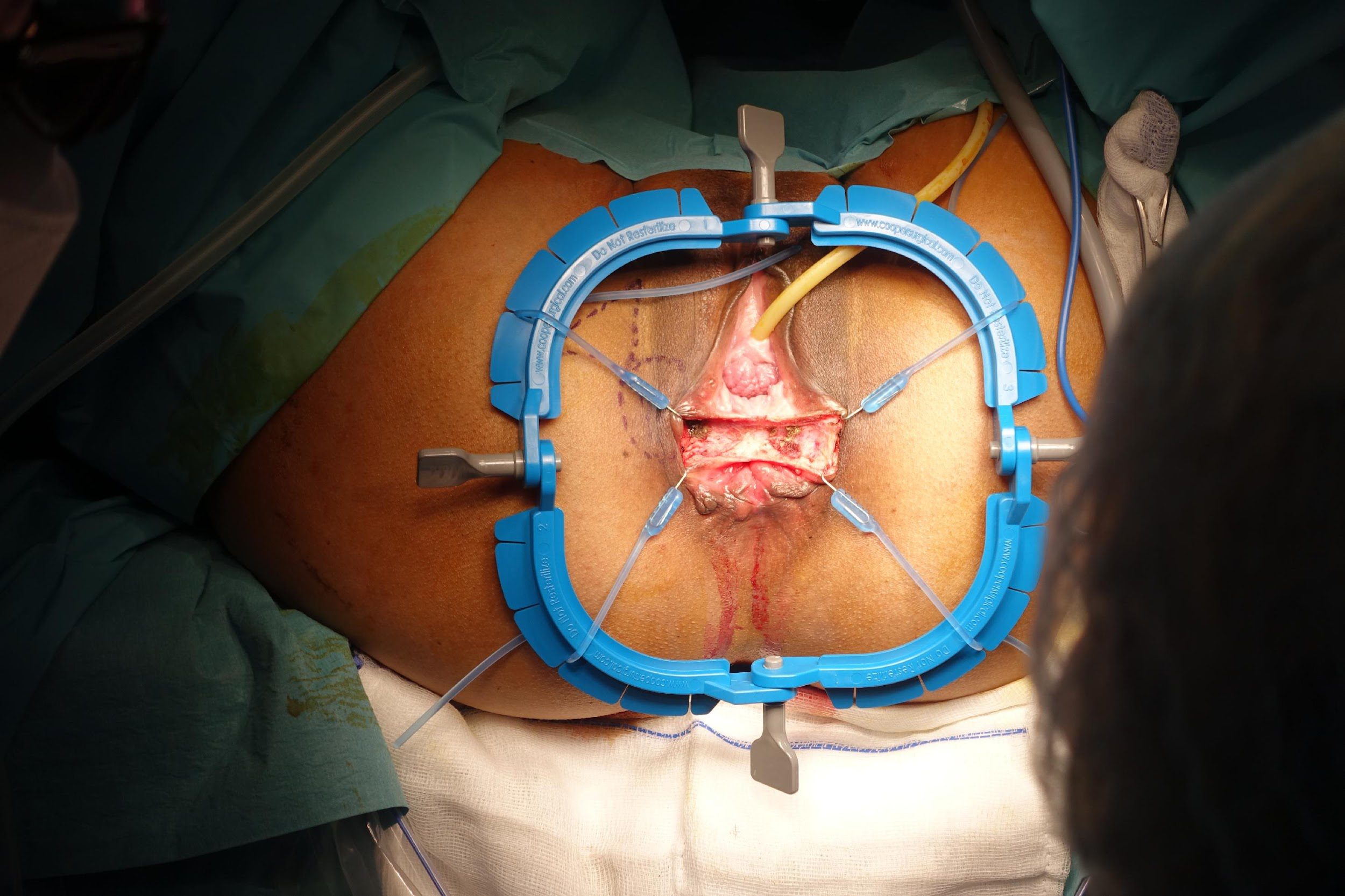
these photos contain sensitive content which some people may find offensive and disturbing
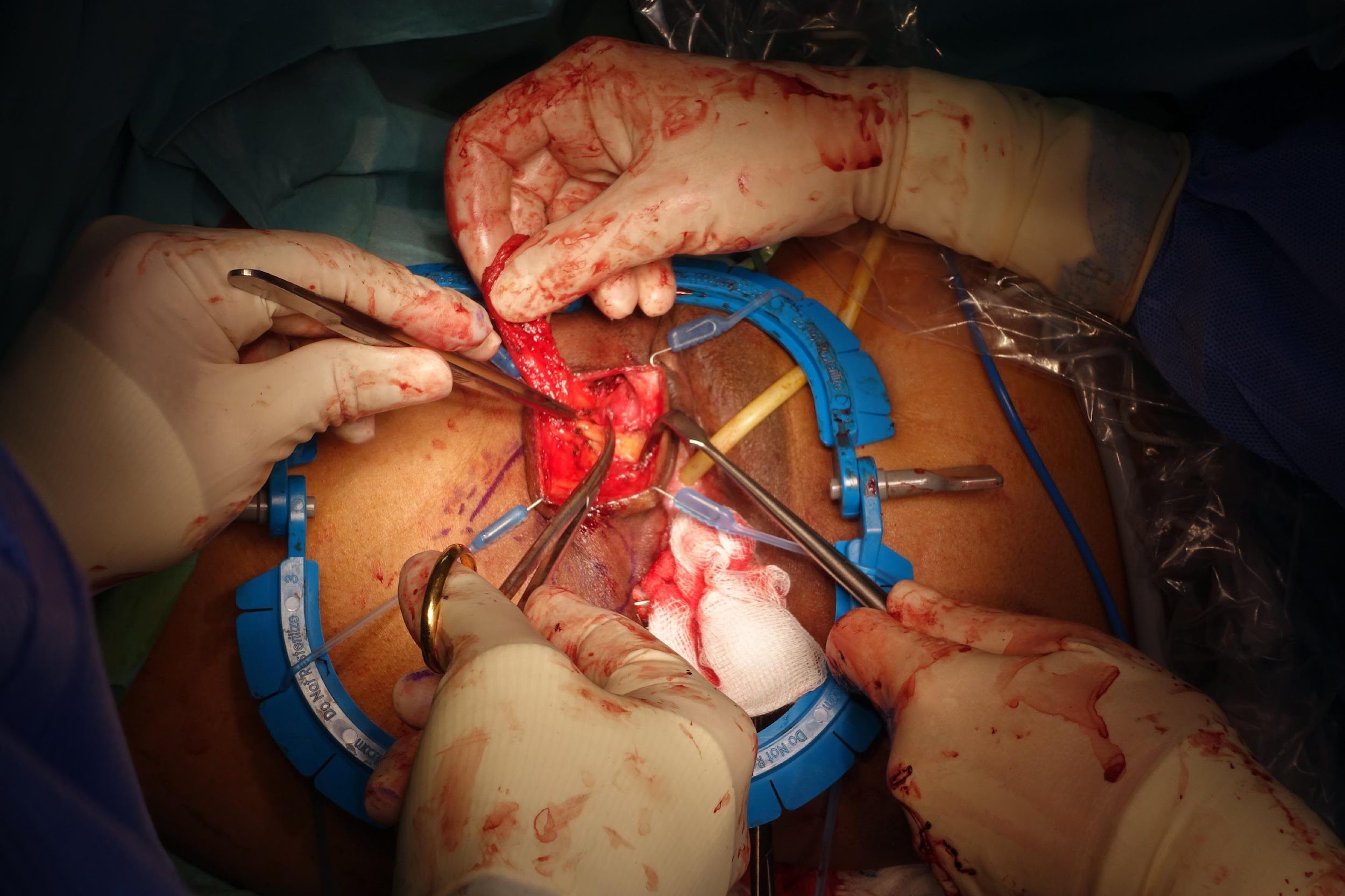
these photos contain sensitive content which some people may find offensive and disturbing
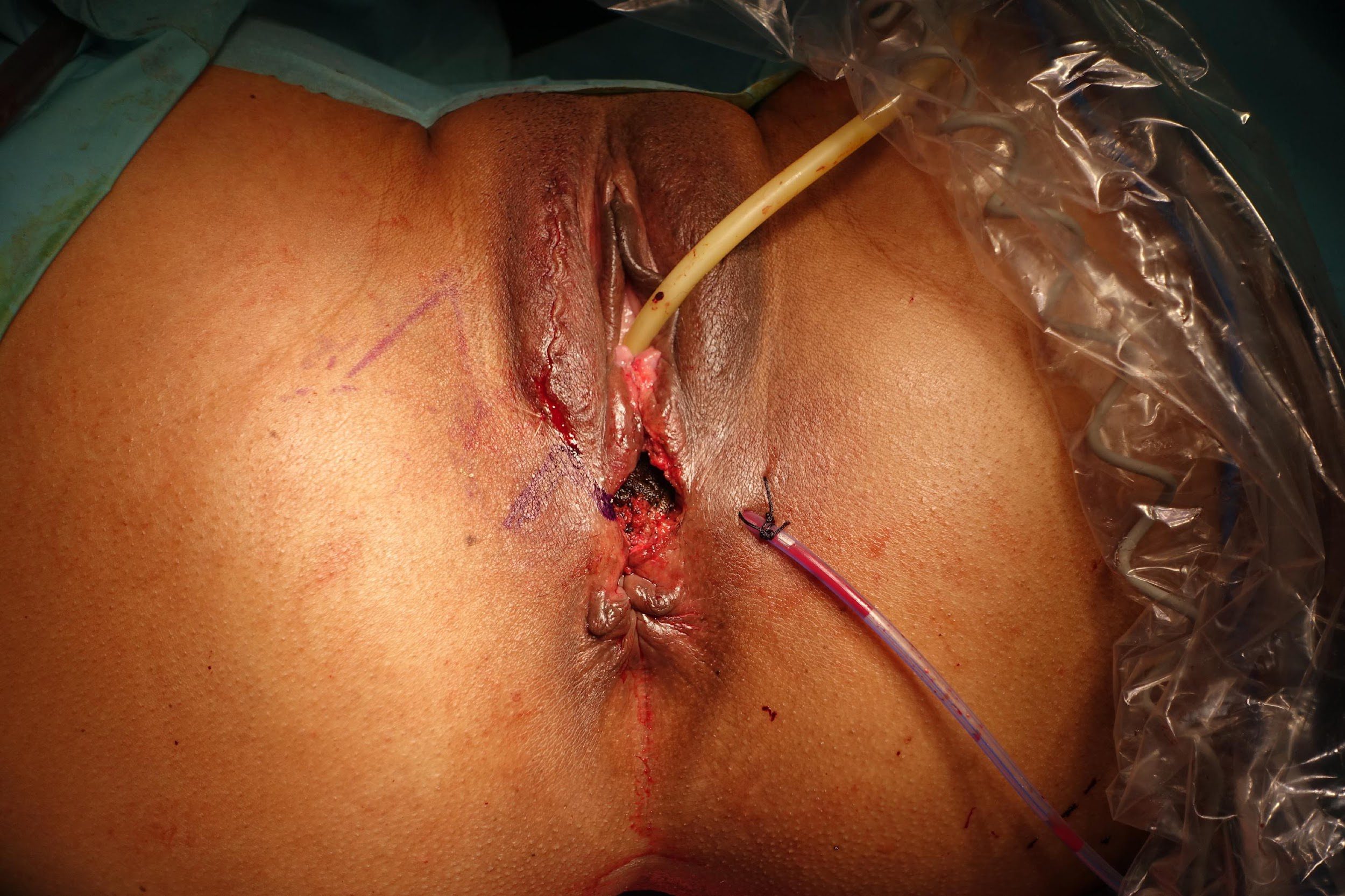
these photos contain sensitive content which some people may find offensive and disturbing
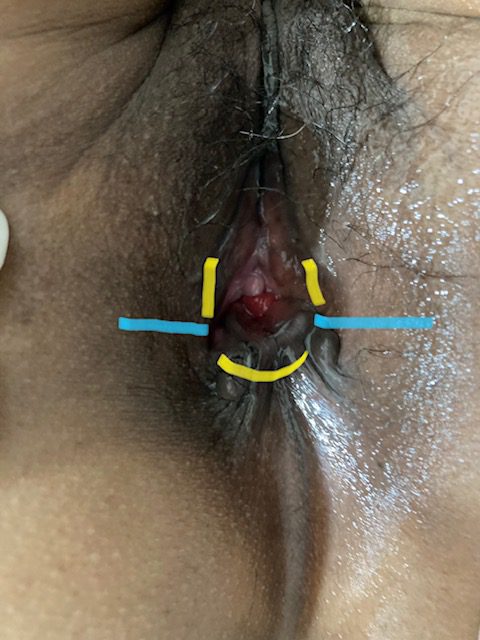
these photos contain sensitive content which some people may find offensive and disturbing
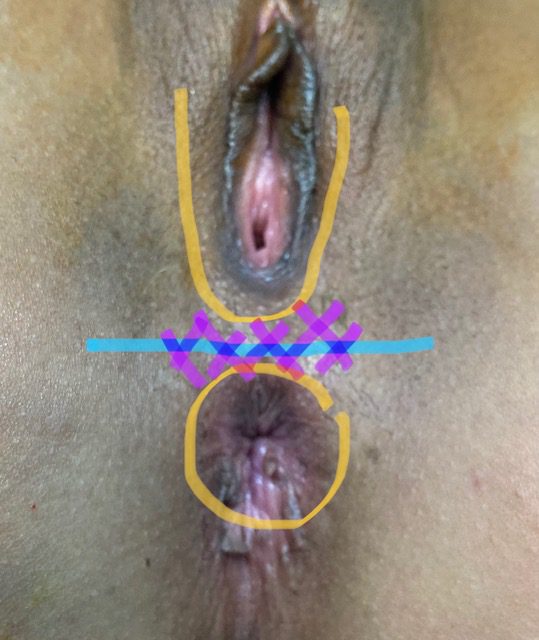
these photos contain sensitive content which some people may find offensive and disturbing
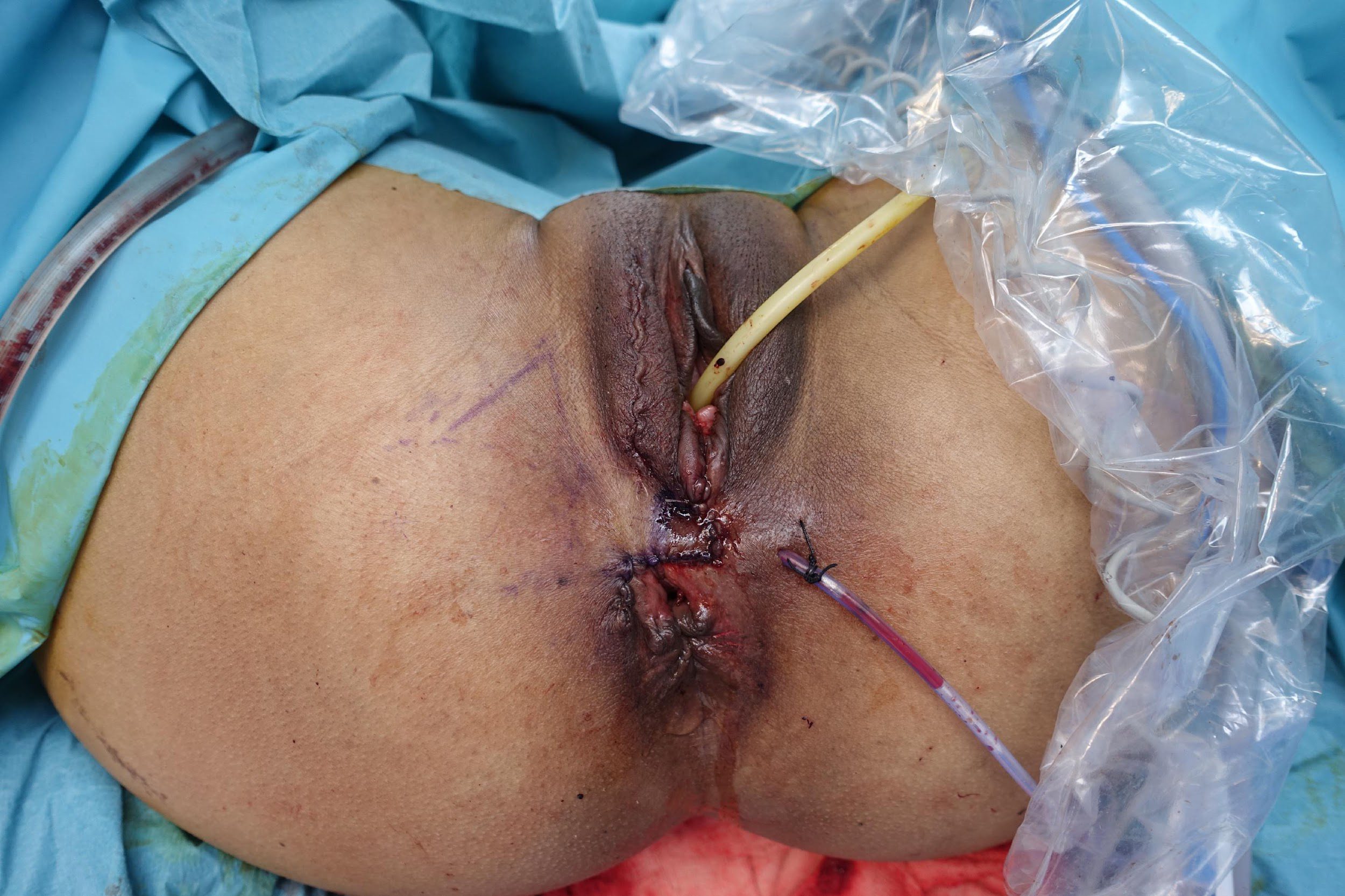
these photos contain sensitive content which some people may find offensive and disturbing
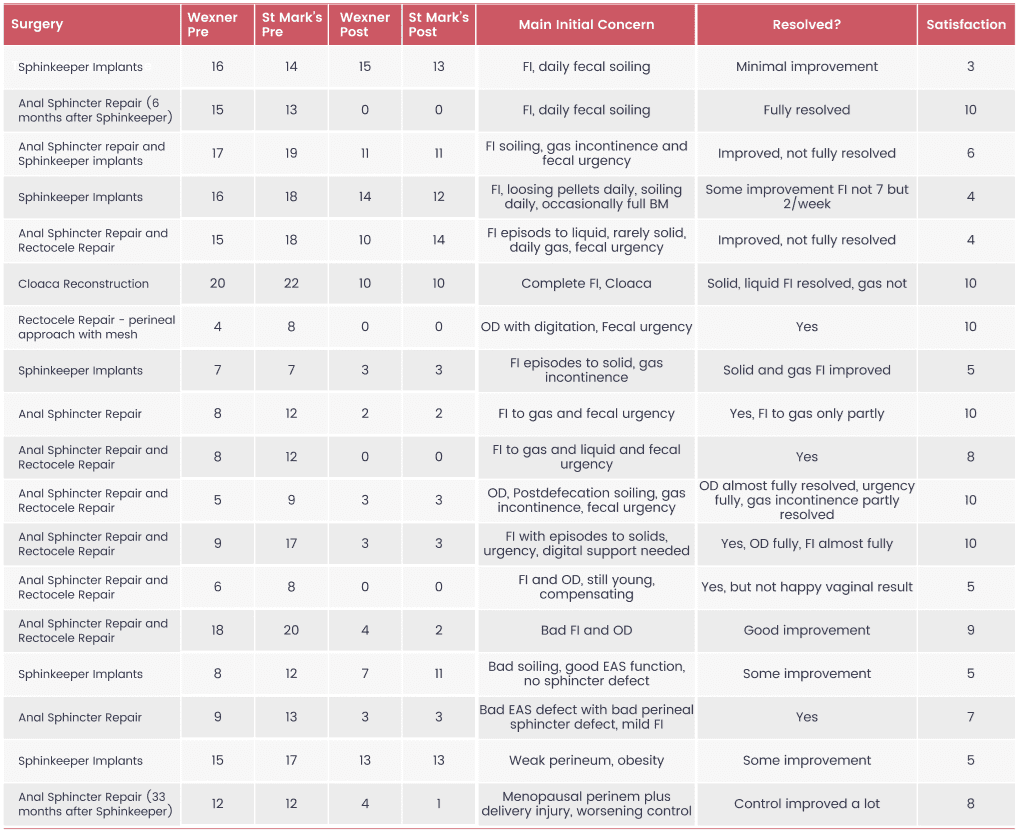

47.5 (35-64) years
16:1
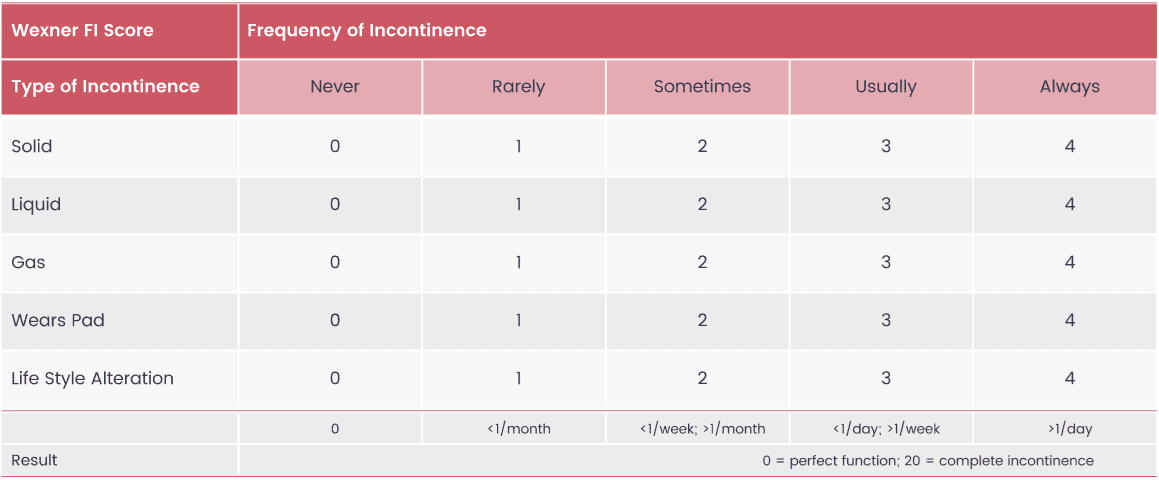
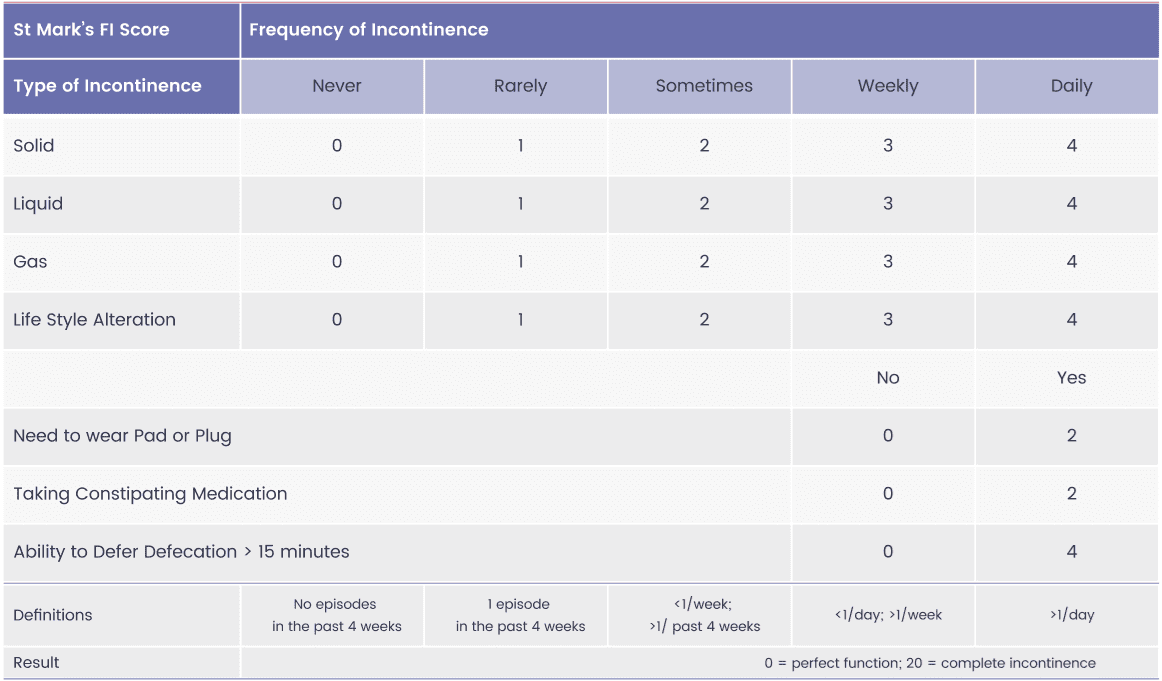
10.5/20 points
13.9/24 points
5.66/20 points
5.61/24 points
7.1 points


